APVV 0028-07
Project of Slovak Research and Development Agency APVV 0028-07
Dynamics of development and resistance mechanisms on betalactams and quinolones
in animal Escherichia coli
(Duration: 9.2008-12.2010)
The main aim of the project is obtaining a new knowledge about development dynamics and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms (betalactams and quinolones) in animal Escherichia coli.
Characterisation of expected resistance mechanisms ((blaTEM, ESBL, CTX-M, gyrA and parC, plasmid quinolone resistance) will be oriented on classic PCR reaction with DNA sequencing and on intepretative reading of minimal inhibitory concentrations animicrobial agents. Molecular subtypisation of resistant Escherichia coli strains will be concentrate on virulence factors (adhesins, enterotoxins, verotoxins, invasivity and siderophores) and DNA fingerprinting (rep-PCR, ERIC PCR, plasmid profiling). Practical utilizability of results will be in veterinary diagnostics and therapy and in the education veterinary students and surgeons.
Methodology
We used veterinary version of Midivet kit for investigation of minimal inhibitory concentrations (Gattringer, Niks et al. 2002) from Bel-Miditech Bratislava (Table 1).
Table 1. Composition and extent of dilution series of antimicrobial agents in MidiVet kit for Escherichia coli including interpretation criteria (CLSI, 2008) for resistance assesment in terms minimum inhibitory concentration
| Antimicrobial agent | Range of dilution | Susceptible | Resistant |
| (g/ml) | (g/ml) | (g/ml) | |
| Ampicillin (AMP) | 0.564 | ≤16 | ≥32 |
| Ampicillin+sulbactam(A+IB) | 0.5+0.2-64+32 | ≤16+8 | ≥32+16 |
| Ceftiofur (CFF) | 0.12-16 | ≤4 | ≥8 |
| Cefquinome (CFQ) | 0.25-32 | ≤16 | ≥32 |
| Ceftriaxon (CTR) | 0.5-64 | ≤32 | ≥64 |
| Ceftazidime (CAZ) | 0.2-32 | - | - |
| Gentamicin (GEN) | 0.25-32 | ≤4 | ≥8 |
| Kanamycin (KAN) | 0.25-32 | ≤16 | ≥32 |
| Streptomycin (STM) | 1-128 | ≤32 | ≥64 |
| Neomycin (NEO) | 0.5-64 | ≤16 | ≥32 |
| Nalidix acid (NAL) | 1-128 | ≤16 | ≥32 |
| Ciprofloxacin (CIP) | 0.03-4 | ≤2 | ≥4 |
| Enrofloxacin (ENR) | 0.12-16 | ≤1 | ≥2 |
| Chloramfenicol (CMP) | 0.25-32 | ≤16 | ≥32 |
| Florfenicol (FLO) | 0.25-32 | ≤8 | ≥16 |
| Tetracycline (TTC) | 0.25-32 | ≤8 | ≥16 |
| Cotrimoxazol (COT) | 0.1+1.9-3+61 | ≤3+61 | >3+61 |
Goals
- To determine development of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms to betalactamase and qiunolone in commensal and pathogenic E. coli.
- Phenotypic and genotypic identification of resistance mechanisms in E. coli, classic betalactamases with low and high resistance value (TEM-1,2/SHV-1), betalactamases with wide spectrum ESBL-TEM, ESBL CTX-M, mechanisms of chromosomal quinolone resistance (gyrA and parC) and plasmid quinolone resistance and other groups of antimicrobial substances (genes of resistance tet, cat, cml, flo, sul, aac) and integron detection.
- Subtypisation of resistant E. coli strains for epidemiological determination.
- Disseminations of results in Veterinary service and strategy to decreasing the range of antimicrobial resistance development in gramnegative bacteria.
Project phases
- VE01: Dynamics of E. coli antimicrobial resistance development and phenotype determination of resistance mechanisms in animal. (09/2008-06/2009)
- VE02: Genotypic determination of E. coli resistance mechanisms. (09/2008-10/2009)
- VE03: E. coli subtypization for epidemiological investigations. (12/2008-10/2010)
- VE04: Creation of E.coli antibiotic resistance mechanisms in slovak veterinary database . (09/2008-12/2010)
Summary of results (2008-2010)
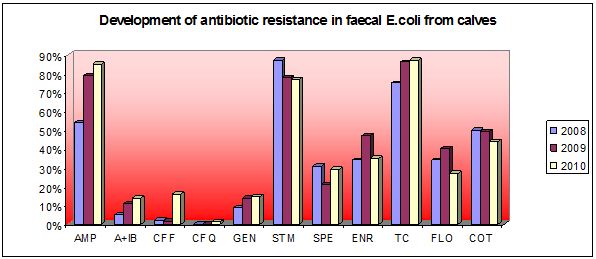
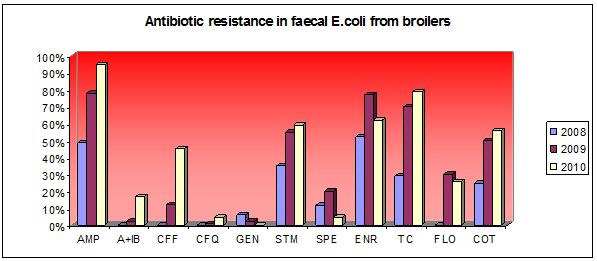
The rapid increasing of occurence Escherichia coli resistance on veterinary cephalosporins (ceftiofur and cefquinome) and occurence of ESBLs (extended spectrum of betalactamases) were recorded. The high level MIC of enrofloxacin in animal E.coli was the highest in EU members. Genes of ESBL (CMY-2, CTX-M) were ussually associated with the presence of mobile elements: transposon Tn3, insertion sequence ISEcp1 and/or integron 1. Gene of CTX-M1 in calf E.coli was on plasmid F1B. The presence of pandemic serotype ST131 associated with genes CTX-M1 group were recorded in one broilers and three calf strains. Maldi tof analysis revelaed that one broilers and one calf strains were clonally related in dendrogram (poultry farm and calves farm was in the same region). The occurence of qnrS1 gene in poultry strain E.coli (with high level of MIC on fluoroquinolones) was first time described in Slovakia. DNA sequence of qnrS1 gene was assessed in GenBank No. GQ162867.
The most occuring tetA and tetB genes were detected in E.coli from calves and poultry. Sulfonamide genes sul1, sul2, sul3, trimethoprim resistance dfrA and streptomycin resistance genes aadA were ussually associated with integron 1. Genes floR (florfenicol) were usssually associated with chloramphenicol genes cm1 and cat. Phylogenetic analysis of poultry strains revealed that both commensals (A, B1) and pathogens (B2, D) contained virulence factors of APEC (aviary pathogenic E.coli). Project results are assessed on web page Slovak Antimicrobial Resistance Veterinary Database, which were from May 2010 until now, visited 304 times from 75 various IP adresses.
Investigators
From Institute of Animal Physiology Slovak Academy of Sciences, Kosice:
Principal Investigator:
Prof. DVM. Vladimir Kmet, DSc. - kmetv@saske.sk
References
- Kmet V., Niks M., Zubricky P., Miholics S., Viest M.: Antibiotic resistance in commensal Escherichia coli isolated from pigs. Slovak Veterinary. Journal . 31 (2), 2006, 97-99 (in Slovak)
- Horosova, K., D. Bujnakova, V. Kmet.: The Action of Oregano on Chicken Lactobacilliand E. coli. Folia Microbiologica 51, 2006, 281-282
- Kmet V.., Bujnakova D., Novak S., Melicharek I., Kmetov M: Minimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics in Escherichia coli isolated from diarrhoeic calves. Slovak Veterinary. Journal 32 (1), 2007, 31-33 (in Slovak)
- Gattringer R, M. Niks, R.. Ostertag, K. Schwarz, H. Medvedovic, W.Graninger, A. Georgopoulos, 2002: Evaluation of MIDITECH automated colorimetric MIC reading for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. J Antimicrob. Chemother. 49, 651-659
- Kmet V.: Host-microbial interplay in animal digestive tract and antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli (Scientific monograph in Slovak). Ed. Tribun EU Brno, 2009, 97 pp. ISBN 978-80-7399-554-6.
- Kmet V., Bujnakova D., Novak S.: Development of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from calves in Slovakia (in Slovak). Reporter of Bioveta SK, 2009, No. 6,
p. 6-7, ISSN 1337-6691 - Kmet V., Novak S., Miholics ., Kmetova M. , Hska M.: Enrofloxacin resistance of faecal Escherichia coli in broilers and calves (in Slovak). Slovak Veterinary Journal, 35, No. 1, 2010, 42-43
- Drugdov Z., Kmet V., Bujnakova D.: Virulence factors in Escherichia coli isolated from chicken meat in Slovakia. J. Food and Nutr. Res. 49, 2010, 10-13
VUP - Kmet V., Kmetova M.: High level of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli from healthy chicken broilers. Folia microbiologica 55, 2010, 79-82
SPRINGER - Kmet V., Piatnicov E.: Antibiotic resistance in commensal intestinal microflora. Folia microbiologica. Folia Microbiologica 55, 2010, 332- 335
SPRINGER
Disclaimer & contact person
The information on this site is provided for educational and informational purposes only.
We don`t recommend or endorse any specific products that may be mentioned on the site. Reliance on any information provided by this site is solely at your own risk.
Dr. Vladimir Kmet
webpage: www2.saske.sk/kmetv